Clinical Cases
Macular hole Retina
What is the Macular Hole?
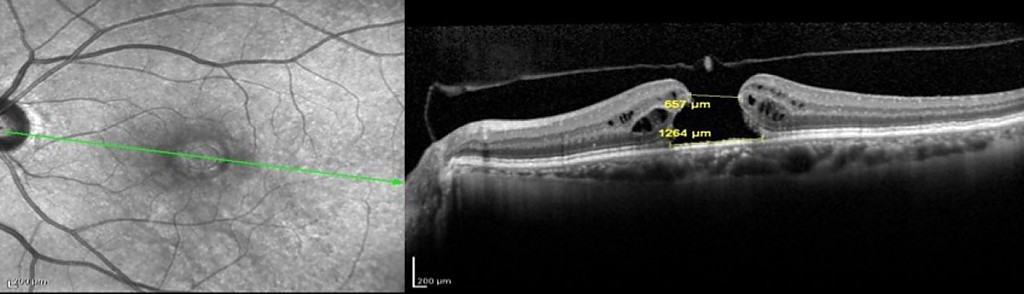
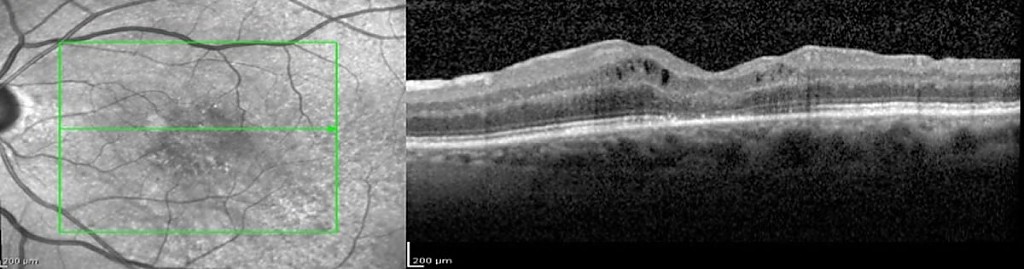
Pathology consisting of the presence of an opening in the macula, which is the central area of the retina. With age, or in some cases, due to trauma, the vitreous humor contracts and separates from the macula. In some cases, this dynamic traction process leads to the avulsion of the retinal tissue, forming a hole in the macula. Initially, the symptoms may condition some distortion of the image. If it progresses, a "black spot" ends up appearing on the central axis of the vision.
How is the diagnosis made?
The macular hole is diagnosed by the ophthalmologist, after the examination of the ocular fundus and an optical coherence tomography (OCT). This test confirms the diagnosis and provides additional anatomical details. Visual recovery will always be better the earlier this pathology is diagnosed and treated.
Treatment
The Macular Hole is treated through a retinal surgery called Vitrectomy. This surgical procedure has a good prognosis, since more than 90% of the cases end up closing.