Clinical Cases
Epiretinal membrane Retina
What is the Epiretinal Membrane?
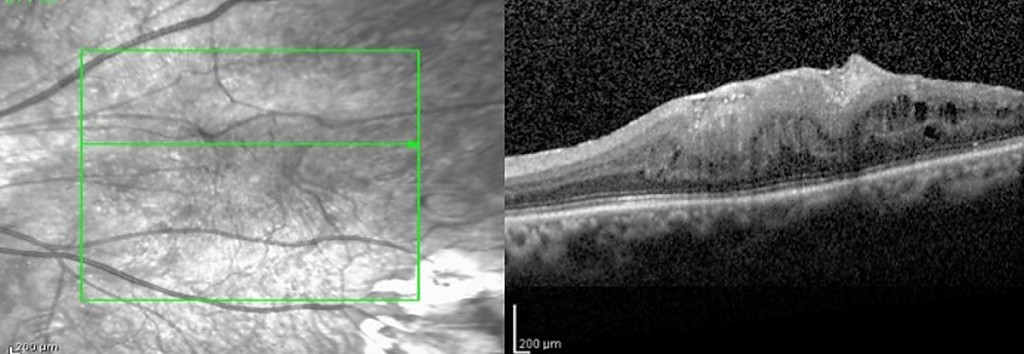
The epiretinal membrane consists of the development of a translucent cell membrane over the central area of the retina (macula). When this membrane contracts, it produces distortion of the retinal tissue and progressive deformation of the retina with consequent visual alteration. The most frequent symptomatology consists of the loss of the vision and the distortion of the images (also denominated metamorfopsia). Diagnosis is made by examining the retina with the slit lamp and quantifying the degree of evolution through optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Treatment
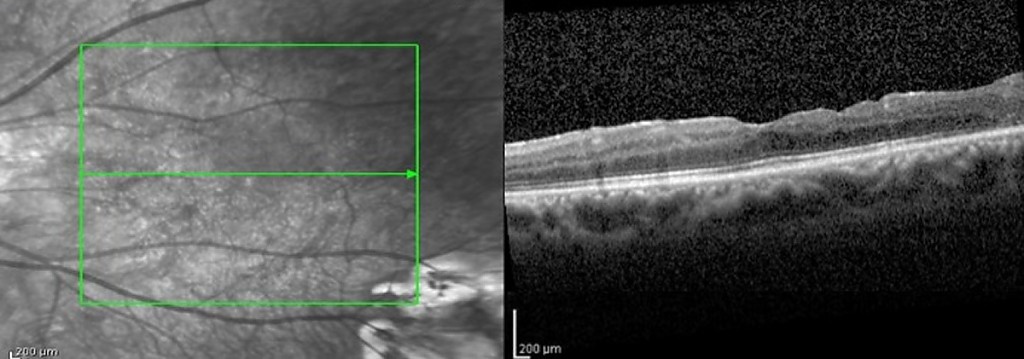
When there is a progressive decrease in vision, or if the perception of object distortion increases, the membrane can be removed through retinal surgery (vitrectomy). The macula resumes its anatomy and the vision recovers progressively, after the removal of this structure.